
The external ear is a focus of otologic and plastic surgery, but it is also important in neurologic and lateral skull-base surgery. It is also cosmetically important and its anatomical structures are extremely complicated and delicate.

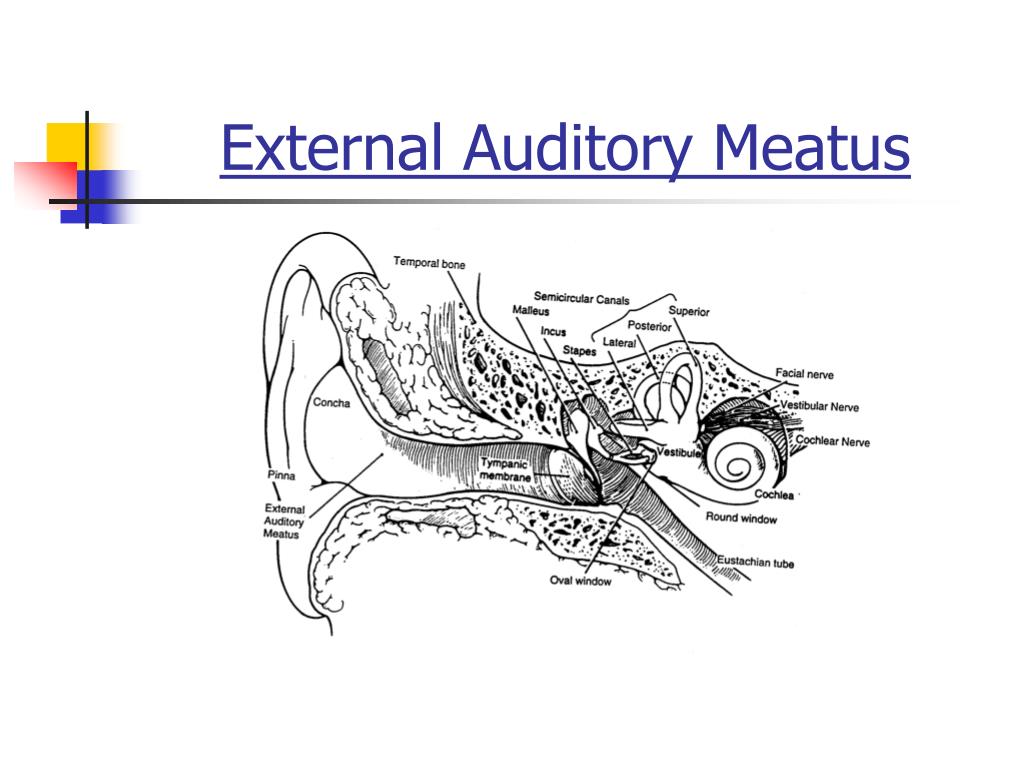
The auricle is a concave structure that directs sound waves into the external acoustic meatus. The external ear is formed by the auricle, external acoustic meatus, and tympanic membrane. The lymphatic drainage of the external ear is to the superficial parotid, mastoid, upper deep cervical and superficial cervical nodes.Noritaka Komune, Junichi Fukushima, and Albert L. Some individuals can complain of an involuntary cough when cleaning their ears - this is due to stimulation of the auricular branch of the vagus nerve (the vagus nerve is also responsible for the cough reflex).
#External acoustic meatus skin
Auriculotemporal nerve (branch of the mandibular nerve) - innervates the skin of the auricle and external auditory meatus.Lesser occipital nerve (branch of the cervical plexus) - innervates the skin of the auricle.Greater auricular nerve (branch of the cervical plexus) - innervates the skin of the auricle.The sensory innervation to the skin of the auricle comes from numerous nerves: Venous drainage is via veins following the arteries listed above. Maxillary artery (deep auricular branch) - supplies the deep aspect of the external acoustic meatus and tympanic membrane only.The external ear is supplied by branches of the external carotid artery: The parts of the tympanic membrane moving away from the lateral process are called the anterior and posterior malleolar folds. The handle of malleus continues superiorly, and at its highest point, a small projection called the lateral process of the malleus can be seen. On the inner surface of the membrane, the handle of malleus attaches to the tympanic membrane, at a point called the umbo of tympanic membrane. The translucency of the tympanic membrane allows the structures within the middle ear to be observed during otoscopy. The membrane is connected to the surrounding temporal bone by a fibrocartilaginous ring. It is a connective tissue structure, covered with skin on the outside and a mucous membrane on the inside. The tympanic membrane lies at the distal end of the external acoustic meatus. It ends by running in an inferoanterior direction.In then turns slightly to move superoposteriorly.Initially it travels in a superoanterior direction.The external acoustic meatus does not have a straight path, and instead travels in an S-shaped curve as follows: The walls of the external 1/3 are formed by cartilage, whereas the inner 2/3 are formed by the temporal bone. The external acoustic meatus is a sigmoid shaped tube that extends from the deep part of the concha to the tympanic membrane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
